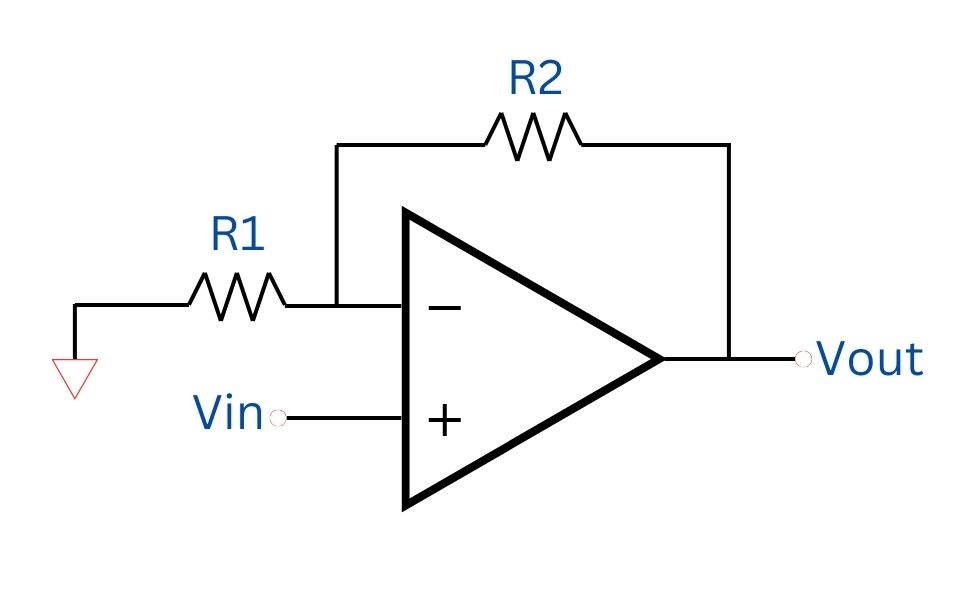
Theory
A non-inverting amplifier is a basic yet powerful configuration in the field of operational amplifiers (op-amps). It is widely used in various electronic applications due to its ability to amplify input signals without inverting the phase. In this explanation, we will explore the theory behind a non-inverting amplifier using an op-amp, two resistors (R1 and R2), with the input voltage denoted as Vin and the output voltage as Vout.
Circuit Configuration
The non-inverting amplifier circuit consists of:
- Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp): The central component that amplifies the input signal.
- Resistors R1 and R2: These resistors set the gain of the amplifier.
In this configuration:
- The input voltage Vin is applied to the non-inverting input terminal (+) of the op-amp.
- The inverting input terminal (-) is connected to a voltage divider formed by R1 and R2, with the feedback loop connecting the output Vout to this voltage divider.
How It Works
- Input Stage: The input signal Vin is applied directly to the non-inverting input of the op-amp. This means the input voltage is the same as the voltage at the non-inverting terminal.
- Feedback Loop: The output voltage Vout is fed back to the inverting input through the voltage divider formed by resistors R1 and R2. The voltage at the inverting input (V-) is a fraction of Vout determined by the ratio of R1 and R2.
- Voltage at Inverting Input: The voltage V- at the inverting input is given by:
V- = Vout*(R1/(R1+R2))
- Op-Amp Behavior: The op-amp adjusts Vout to make the voltages at the inverting and non-inverting inputs equal. Therefore, V- = V+. Given V+ = Vin , we have:
Vin = Vout*(R1/(R1+R2))
- Output Voltage Equation: Rearranging the above equation to solve for Vout, we have:
Vout = Vin *(1+(R2/R1))
This equation shows that the output voltage Vout is the input voltage Vin multiplied by the gain factor, which is determined by resistors R1 and R2.
Gain of the Amplifier
The gain Av of a non-inverting amplifier is given by:
Av = Vout/Vin = 1 + (R2/R1)This indicates that the output voltage is the input voltage scaled by the gain factor. The gain can be adjusted by changing the values of resistors R1 and R2.
Summary
A non-inverting amplifier using an op-amp, two resistors R1 and R2, amplifies the input voltage Vin without inverting its phase.
Mathematically, we can express the Non-Inverting Amplifier equations as:
Vout = Vin × (1 + (R2 / R1))
Vin = Vout / (1 + (R2 / R1))
R1 = R2 / ((Vout / Vin) - 1)
R2 = ((Vout / Vin) - 1) × R1
The Non-Inverting Amplifier Calculator uses the equations above to find each parameter that's required as long as three out of four of the parameters are provided.